Olaf Hartig | RDF Star: Metadata For RDF Statements
KGC | The Complete Collection
•
22m
The lack of a convenient way to capture annotations and statements about individual RDF triples has been a long standing issue for RDF. Such annotations are a native feature in other contemporary graph data models (e.g., edge properties in the Property Graph model). In recent years, the RDF* approach has emerged to address this limitation of RDF. After RDF* gained traction among both vendors and users of RDF systems, a community group has formed to produce a specification of the approach, now called RDF-star. In February 2021, the group published a first working draft of this spec, which is accompanied by several test suites. This presentation will introduce the approach and the various features that it adds to RDF and SPARQL.
Up Next in KGC | The Complete Collection
-
Paco Nathan | Graph Based Data Science
Python offers excellent libraries for working with graphs: semantic technologies, graph queries, interactive visualizations, graph algorithms, probabilistic graph inference, as well as embedding and other integrations with deep learning. However, most of these approaches share little common groun...
-
Paolo Manghi | The OpenAIRE Research ...
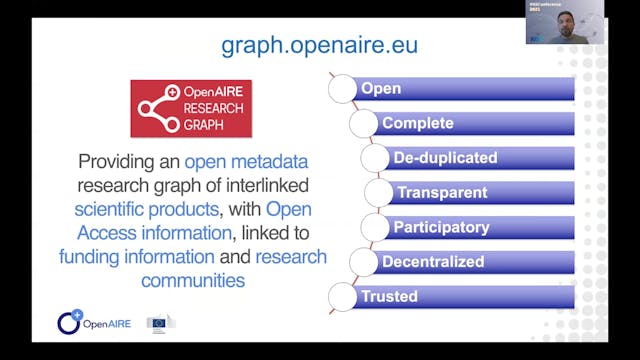
The presentation will introduce the motivations, architecture, and operation of the OpenAIRE Research Graph (http://graph.openaire.eu), one of the largest (if not the largest) public, open access, collections of metadata and semantic links (~1Bi) between research-related entities: articles (124M+...
-
Peter Hicks | Visualizing Data Lineage
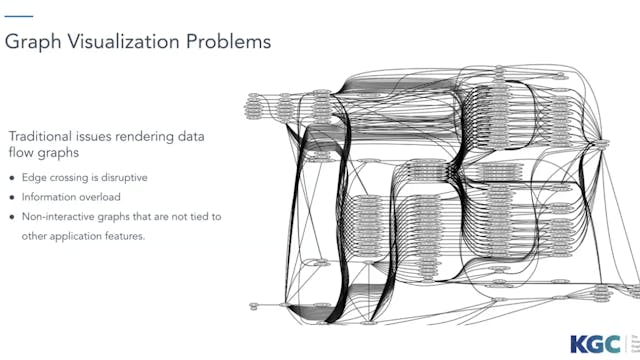
Extracting metadata from data pipelines and building useful graphs for real production environments.